| News | Events | Sites | Database | Knowledge Base | Forum |
|
General objective of this concept note Population, population growth and food production Agriculture: what role for development, which linkages with water? Water for agriculture: where do we stand? Which future? Water for agriculture: which may be the priorities? Annex I. Background data ANNEX I. BACKGROUND DATA Introduction Throughout the concept note a distinction has been made in developed countries, emerging countries and least developed countries. In addition a distinction has been made in the Continents. The distinction in types of countries is based on the publications of the UN Organisations and other globally working institutions. This resulted in the following:
The agricultural land covers about 1.5 billion ha, which is about 11% of the global land surface of 13.3 billion ha. With respect to agriculture four types of cultivation practices may be distinguished, viz.:
With respect to agriculture a distinction can be made in three agro-climatic zones:
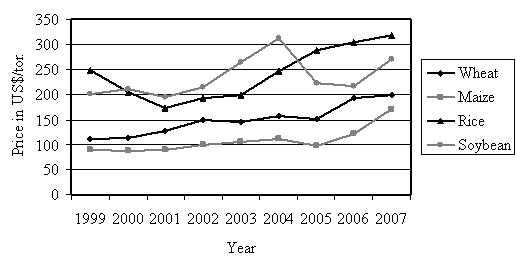
Population and population growth Based on the data of the UN Population Reference Bureau and the distinction in types of countries and in Continents Tables I.1 and I.2 show some characteristic data with respect to population, population density and water management. Some characteristic data on food production Development of World Market prices for the four main food crops are shown in Figure I.1.
Figure I.1. Development of prices for four basic food crops since 1999 (Source: IMF) Some characteristic average data with respect to cereal production are shown in Figure I.2.
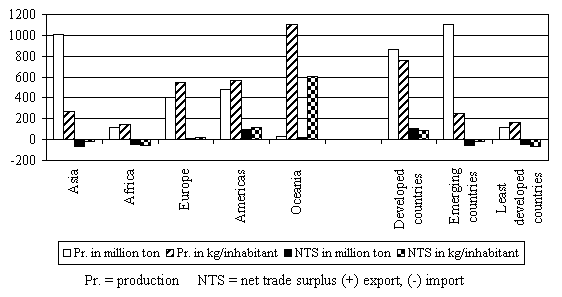
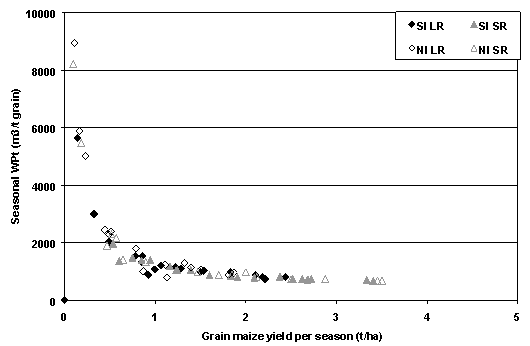
Figure I.2. Some characteristic average data with respect to cereal production (Schultz, et al., 2005) (Source of the data, FAO Food Outlooks) Some characteristic data on the relation between water use and yield There seems to be an interesting relation between water use and yield. An example, based on the cultivation of maize, is shown in Figure I.3. Here it is shown that below a yield of about 2 tons/ha for maize, the water use per ton of crop increases rapidly, especially due to the evaporation from the ground.
Figure I.3. Relation between yield and water use in m3 per ton of grain for maize. |